...
- At the bottom of the Symbology pane, click the Geoprocessing tab.
- At the top of the Geoprocessing pane, click the Back arrow button.
- Within the Interpolation toolset, click the Natural Neighbor tool.
- Beginning with step 5, repeat all steps in the 'Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation Method' section above, but rename the raster output “NN_Rain”.
...
- At the top of the Geoprocessing pane, click the Back arrow button.
- Collapse the Spatial Analyst Tools toolbox.
- Click the 3D Analyst Tools toolbox > Data Management toolset > TIN toolset > Create TIN tool.
- For ‘Output TIN’, type “TIN_Rain” and click elsewhere to update the text field.
- For ‘Coordinate System’, use the drop-down menu to select the Rainfall feature class, which will import the same coordinate system used to map the original latitude and longitude data of the rain gauges.
...
- At the top of the Geoprocessing pane, click the Back arrow button.
- Within the 3D Analyst Tools toolbox, collapse the Data Management toolset.
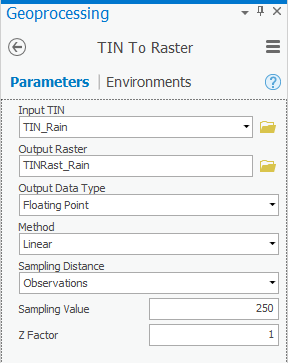
- Within the 3D Analyst Tools toolbox, click the Conversion toolset > From TIN toolset > TIN To Raster tool.
- For ‘Input TIN’, use the drop-down box to select the TIN_Rain TIN.
- For ‘Output raster’, rename the exported raster from “tin_rain_tin” to “TINRast_Rain”.
- Ensure that your 'TIN To Raster' tool Parameters tab appears as shown below and click Run.
- In the Contents pane, uncheck the TIN_Rain layer to view the new raster layer created from the TIN.
- Repeat the steps 11-16 above in within the 'Inverse Distance Weighted Interpolation Method' section on page 12 above to symbolize the TINRast_Rain layer as you did the other raster layers.
...
- In the Contents pane, check the Hurricane layer to make it visible.
- At the top of the Geoprocessing pane, click the Back arrow button.
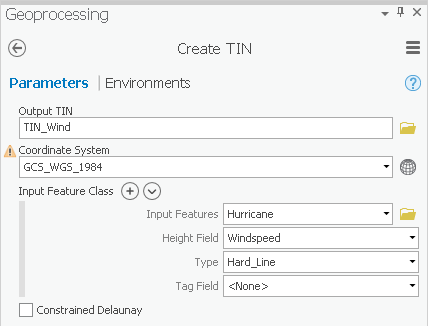
- In ArcToolbox navigate to 3D Analyst Tools toolbox > Data Management toolset > TIN > Create TIN.
- For ‘Output TIN’, type “TIN_Wind” and click elsewhere to update the text field “TIN_Wind”.
- Use the ‘Input Feature’ drop-down box to select the Hurricane feature class.
- Use the ‘Height Field’ drop-down box to select the Windspeed field as shown below.
- Use the ‘Coordinate System’ drop-down box to select the Houses layer.
- Ensure that your 'Create TIN' tool Parameters tab appears as shown below and click Run.
...
- Repeat steps 9-16 above in the TIN Interpolation Method section on pages 15 and 16above, but select TIN_Wind for the input TIN and name the output raster “TINRast“TINRast_Wind”Wind”.
- In the Contents pane, click the arrow next to all of the raster and TIN layers to collapse their symbologies.
...
Extracting Multi Values to Points
- In the Toolboxes tab, click the collapse the 3D Analyst Tools toolbox to collapse it.
Before extracting data, you must define the projections of the TIN raster layers.
- .
- Click Spatial
- Click Data Management Tools > Projections and Transformations > Define Projection
- In the ‘Input Dataset or Feature Class’ drop-down box, click TINRast_Rain.
- For ‘Coordinate System’, click the icon to the right of the box, shown below.
- Double-click Geographic Coordinate Systems to expand it. Scroll down to World, and double-click World. Select WGS 1984. Click OK. Ensure that the ‘Define Projection’ window appears as shown below and click OK.
- Repeat steps 3-7 for TINRast_Wind, except for the ‘Input Dataset or Feature Class’ drop-down select TINRast_Wind.
- Click Spatial Analyst Tools > Extraction > Extract Multi Values to Points.
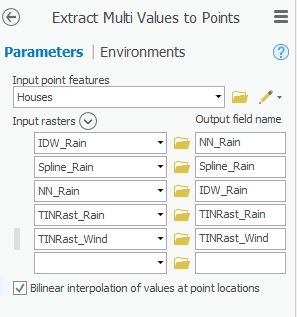
- Use the ‘Input point features’ drop-down box to select the Houses layer.
- Use the ‘Input rasters’ drop-down box to select all five interpolation rasters you created earlier one at a time: IDW_Rain, Spline_Rain, NN_Rain, TINRast_Rain and TINRast_Wind. The order in which the rasters are listed is the same order in which the extracted value columns will appear in the output feature class attribute table.
- Check Bilinear interpolation of values at point locations.
- Ensure Ensure that your ‘Extract 'Extract Multi Values to Points’ window Points' tool Parameters tab appears as shown below and and click Run.
The Extract Multi Values to Points tool simply adds a field for the value of each raster to the end of your existing Houses attribute table, which is why you were not asked for an output location.
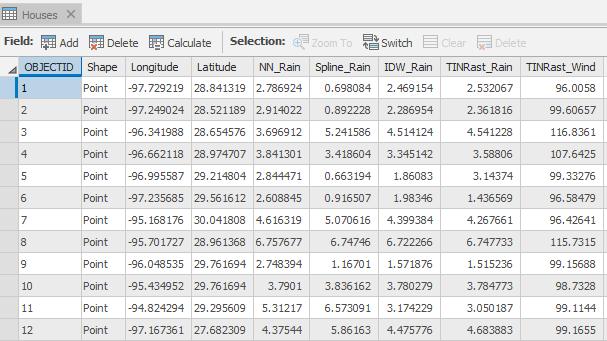
- In the Contents pane, right-click the Houses layer and select Attribute Table.
Notice the five new fields added to the end of the existing attribute table which contain the values of each of the five rasters at each house location. Notice also the differences in rainfall estimates resulting from the four different interpolation techniques. At many house locations, the value of the Spline interpolation is the most different from the other interpolation method values.
You are now ready to export the data table into a format that can be used by the insurance company without having to use ArcGIS software.
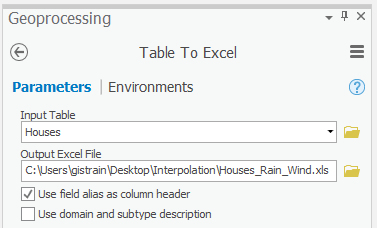
- Click Conversion Tools > Excel > Table To Excel.
- Use the ‘Input Table’ For ‘Input Table’, use the drop-down box menu to select the Houses attribute table.
The output table location defaults to your project folder.
- For ‘Output Excel File’, replace rename the Excel file from “Houses_TableToExcel” with “Housesto “Houses_Rain_Wind”Wind”.
- Check Use field alias as column header.
- Ensure Ensure that your ‘Table To Excel’ pane looks like that shown below and click 'Table To Excel' tool Parameters tab appears as shown below and click Run.
Now you have what the insurance company is looking for: a single text file containing the locations of the houses in question, as well as the corresponding rainfall and wind speed estimates to use in completing a damage quote for your customers.
...
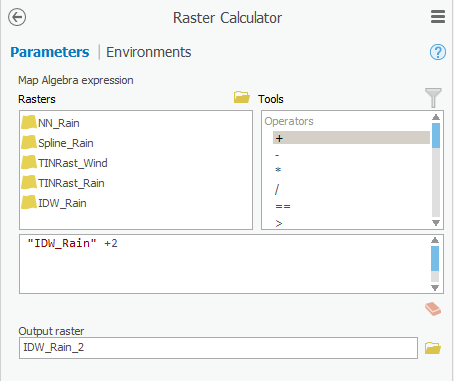
- In the Geoprocessing pane, in the Spatial Analyst Tools toolbox, dou click the Map Algebra toolset > Raster Calculator tool.
- Under ’Rasters’, double-click the IDW_Rain layer.
- Under ‘Operators’, click the + operator.
- For ‘Output raster’, rename the exported raster from “idw_rain_ras” to “IDW_Rain_2”.
- Ensure your ‘Raster Calculator’ window looks like that shown below and click Ensure that your 'Raster Calculator' tool Parameters tab appears as shown below and click Run.
You have now learned multiple methods of interpolating point and line data into raster data and extracting that raster data at corresponding point locations. You have also reviewed skills from other short courses, including mapping Mapping Locations Using XY dataCoordinates.