...
- Right-click the PrecipStations_Layer layer and select Data > Export Features.
Because you last exported a text file outside of your geodatabase, notice the output feature class is now set to a shapefile in your Lab 2 folder, rather than a feature class within your ElevationRainfall geodatabase. - Next to ‘Output feature class’, click the Browse button.
- Navigate to the to the HydrologyLab geodatabase geodatabase.
- Double-click your your HydrologyLab geodatabase geodatabase to save your feature class in it.
- For ‘Name:’, type “PrecipStations_Features” and and click Save Save.
...
- Click Run.
Since you are now using a permanent feature class, you may remove your temporary Events layer and the corresponding Excel table. - Right-click the the PrecipStations_Layer layer and layer and select Remove Remove.
- Right-click the PrecipStations the PrecipStations table and and select Remove Remove.
Projecting vector data
Repeating the technique you learned earlier in this lab to project vector data, project the PrecipitStations layer into the State Plane Texas South Central projection.Save the resulting feature class and name it “PrecipStations_StatePlane”. Remove the original PrecipStations layer from the Table of Contents.
...
- In the Table of Contents, Ctrl-select the PrecipStations_StatePlane and Watersheds_StatePlane layers.
- Right-click either selected layer and select Zoom To Layers.
- Open Geoprocessing pane by clicking Tools from Analysis tab.
- Double-click the Analysis toolbox à Proximity toolset à Create Thiessen Polygons tool.
Before populating the variables in this tool, you will change an Environment setting so that the polygons are calculated for the entire region that you just zoomed to. - At the top of the window, click the the Environments button on the right.
- For Extent, use the drop-down menu to to select Current Current Display Extent and go back to Parameters Parameters.
- For ‘Input Features’, drag in the in the PrecipStations_StatePlane layer layer.
- For ‘Output Feature Class’, rename the the feature class from “PrecipStations_StatePlane_Cr” to “PrecipThiessen”.
- Use the ‘Output Fields’ drop-down menu to to select All All fields.
...
- Ensure your ‘Create Thiessen Polygons’ window appears as shown below and click Run.
...
You will notice that polygons now fill the entire Map Display indicating which areas are closest to which rain gages.
...
- Open
...
- the PrecipThiessen
...
- layer attribute table.
Notice that all of the fields that you originally downloaded from CDO are still included, because you selected to output all fields when running the Create Thiessen Polygons tool. If you do not see all of the same fields, re-run the tool and this time output all fields.
...
- Close
...
- the Table.
Intersecting two polygon layers
...
- In the Analysis Tools toolbox, click the Overlay toolset à Intersect tool.
- For ‘Input Features’, drag in the PrecipThiessen and the Watersheds_StatePlane layers.
- For ‘Output Feature Class’, rename it from “PrecipThiessen_Intersect” to “ThiessenWatershedIntersect”.
- Ensure your ‘Intersect’ window appears as shown below and click Run.
...
- Remove the PrecipThiessen layer from the Table of Contents.
- Zoom to the ThiessenWatershedIntersect layer.
The resulting layer integrates all of the boundaries from both the Thiessen polygons and the watersheds, limited to the extent of their overlap. - Open the ThiessenWatershedIntersect layer attribute table.
Notice that the original 8 watersheds have now been divided into 42 sections indicating which areas of each watershed are closest to each rain gage. Let Pk denote the annual precipitation associated with each rain gage and Aik denote the area of the intersected polygon associated with rain gage k and watershed i. The area weighted precipitation associated with each watershed is
...
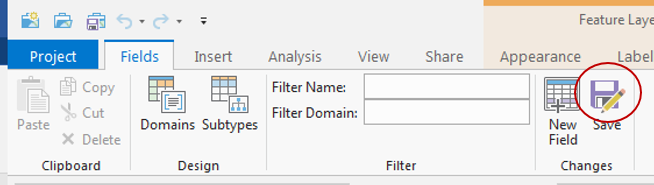
You will add a new field to the table to calculate the elements of the numerator of the equation.|- Click Add Field… button on top of the table display.
...
- For ‘Name:’, type “APProd”.
...
- Use the ‘Type:’, drop-down menu to select Double and click Save on the Fields tab.
...
...
- Right-click
...
- the APProd
...
- field name
...
- and select
...
- Calculate Field.
...
- Using the fields and buttons or by typing, enter
...
- “!ANNPRCPHI! * !Shape_Area!”.
...
Ensure your ‘Field Calculator’ appears as shown below
...
and click
...
Run.
...
The APProd field now contains the numerator values in the equation. You are now ready to summarize the calculated statistics by watershed.
...
Right-click
...
the HU_10_NAME
...
field name
...
and select
...
Summarize….
...
For statistics fields, use the drop-down menu to select
...
the Shape_Area
...
field and select
...
Sum.
...
- Select
...
- the APProd
...
- field and select
...
- Sum.
...
- For ‘Output Table’, rename
...
- the table from “ThiessenWatershedInteract_St” to “WatershedPrecip”.
...
- Ensure your ‘Summarize’ window appears as shown below
...
- and click
...
- Run.
...
The resulting table gives the numerator and denominator in the equation for each watershed.
...
- Open the WatershedPrecip table.
Repeating the techniques you just learned, add a new field to the WatershedPrecip table called “Precip” of type double. Use the field calculator to evaluate [Sum_APProd]/[Sum_Shape_Area]. The result is the precipitation for each subwatershed. Export the table to Excel and format it. Also include the mean annual precipitation over the entire watershed.
...
- Turn off the ThiessenWatershedIntersect layer.
- Right-click the Watersheds_StatePlane layer and select Zoom to Layer.
- Open Toolbox.
- In the Spatial Analyst Tools toolbox, click the Interpolation toolset à Spline tool.
- On the top of the window, click the Environments.
- For Extent, use the drop-down menu to select Current Display Extent.
- Use the ‘Mask’ drop-down menu to select the Watersheds_StatePlane layer.
- Go back to Parameters. For ‘Input point features’, drag in the PrecipStations_StatePlane layer.
- Use the ‘Z value field’ drop-down menu to select the ANNPRCPHI field that contains the values you wish to interpolate.
...
- For ‘Output raster’, rename the exported raster from “Spline_Preci1” to “AnnPrecip”.
...
- Use the ‘Spline type’ drop-down menu to select TENSION.
...
- Ensure your ‘Spline’ window appears as shown below, and click Run.
...
The result is a solid surface estimating the rainfall at each cell, based on the data collected at each rain gage. Turn the Thiessen polygons back on to give them a hollow fill. Symbolize the rain gages as you desire.
FOR MAP LAYOUT TO BE TURNED IN
Create an 8.5 x 11 layout showing the Thiessen polygon boundaries, interpolated rainfall layer and rain gage locations.
Using the techniques you learned earlier in this lab, use the Zonal Statistics as Table tool to export a table containing the total annual rainfall for each watershed, as calculated from the AnnPrecip spline interpolation layer and format the table in Excel.
...