Jane Zhao & Bradley Selke
Digital Media Commons, Fondren Library
last updated Tuesday, March 17, 2015
Outline
- Workshop Objectives
- Introduction
- Photoshop basics
- Photoshop interface
- Cropping images
- Resizing images for different purposes
- Fixing and enhancing images
- Removing a background
- Saving a transparent image
- Adding text and change color
Objectives
Participants will be able to:
- Familiarize with the Photoshop interface
- Crop images with crop tool
- Resize images for web, video, and print
- Use clone stamp tool, sponge tool, and spot healing brush tool
- Use quick selection tool and magic wand tool to make selections
- Understand layers
- Save a transparent image
- Add text and change text color
Introduction
Definition: Photoshop is the predominant photo editing software created by Adobe. It has been used to create images for Internet and Print. Examples include posters, CD covers, online images, etc.
Availability: Photoshop is available for both PC and Mac. As of August 2014, Adobe Creative Suite including Photoshop is only available at the Digital Media Commons and the student lab of Anderson Hall. None of the other student lab computers (colleges, Mudd, Fondren) will have Adobe Creative Suite.
Photoshop Basics
Note: The latest version is Adobe Creative Cloud that requires subscription. This guide was developed using Adobe Creative Suite 5.
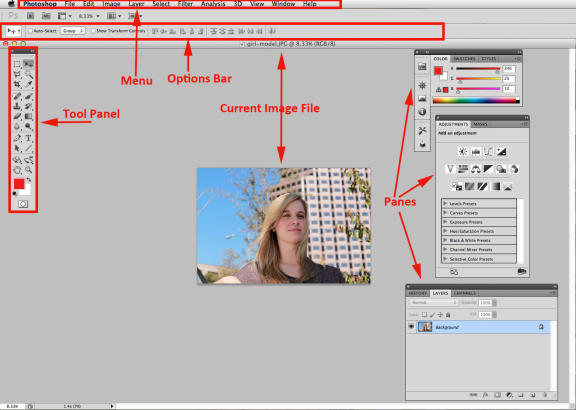
Photoshop Interface
Tool Panel: It contains a bunch of tools for you to edit and create images. These include tools for selecting specific areas of images, cropping images, transforming images, and many more.
Menu: It contains all sorts of options. You can click any menu and see the available functions from the drop-down menu.
Options Bar: It presents different options when different tools are selected. When a tool isn't behaving as you expect it to, the options bar should be the first place you look to fix it.
Panes: Panes can be opened and closed. They display different types of information. If you can't locate a specific pane, go to the Windows menu, and select that pane to open and view it.


Activity 1: Cropping an image
You might want to crop an image if you want to emphasize the subject of the picture or you think there's just too much space around the subject. Activity 1: cropping a picture without using the crop tool bar
- Open the file named girl-model.jpg.
- Click on the Crop tool
 in the tools palette.
in the tools palette. - Drag the cursor over the area of the image.
- Drag the handles to adjust the selection box as necessary.

- Turn on Crop Guide Overlay and select Rule of Thirds, which aids in composing the cropped image. For instance, it is suggested that you place your subject at the crossing of the third. In this portrait, you want the model's left eye to be close to the third crossing.
- Hit Enter/Return key on the keyboard or click the checkmark on top of the window to get rid of the surrounding area.
- To cancel the crop operation, click the Cancel button
 , or right click over the image, from the pop-up menu, choose Cancel.
, or right click over the image, from the pop-up menu, choose Cancel. - To save the cropped image, go to File -> Save as, Format – JPEG, Save as a copy, on the JPEG options window, choose Quality 8 High, then click OK button.
Activity 2: cropping a picture to the dimension of 4"x 6 " (height x width) using the crop tool bar(use girl-model.jpg)
Resizing an image for different uses
Reducing pictures for web use
Reduction is primarily for shrinking images which are too large for publication online. This process causes a loss in information, which is not reversible, so you must remember to back up the original image before you start.
Web pictures are measured in pixels. In general, they are small in file size so that users can view them without any noticeable loading time. To have an idea of image dimensions measured in pixel, take a look at the following three photos:
The highlighted image on Rice homepage is JPEG, 71.91 KB, 746px x 440px available at http://www.rice.edu/_images/_imagery/8-26-nicheranking.jpg

The image close to the bottom of the page is JPEG, 58.5 KB, 253px x 149px available at http://www.rice.edu/_images/_imagery/8-15-broussard.jpg

The Rice logo image is JPEG, 7.02 KB, 48px x 48 px available at https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/428005170/twitshield_normal.jpg

Activity 2: Reducing a picture to 662px x 440px, and about 70KB in file size
- Open the file named red-foliage.jpg.
- Go to menu -> Image Size (or press Shift-Ctrl/-I.) Make sure Scale Styles, Constrain Proportions, and Resample Image are all checked since you want to reduce the image, but not distort the image.
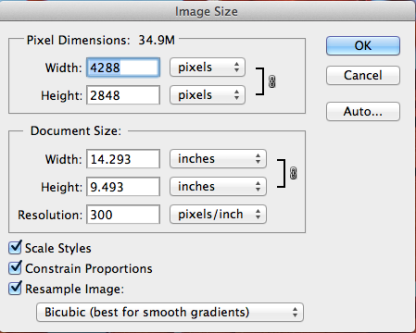
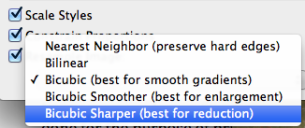
- From the Resample Image drop-down list, choose "Bicubic Sharper (best for reduction)
- Change the height to 440 px, notice the width will be automatically changed to 662 px. Then click OK button.
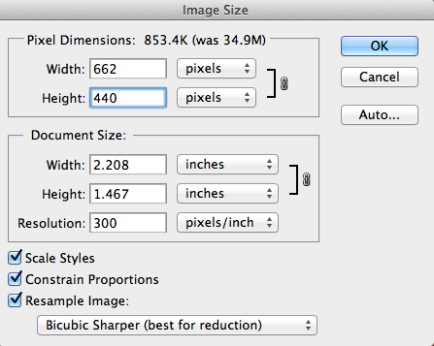
- Go to File -> Save as, Format – JPEG, Save as a copy, on the JPEG options window, slide the slider to the left until you see the file size is about 70K. Then click OK button.
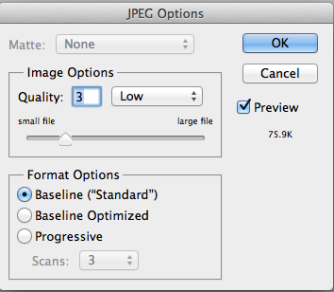
Activity 3: Reducing a picture to 381px x 253px, and about 60KB in file size, and 72px x 48 px, and 10KB in file size respectively.(use red-foliage.jpg)
Resizing pictures for using in iMovie 10.0.4
Movies created in iMovie 10.0.4 are wide screen with dimension of 1920x1080. Pictures in 1920px x 1080px are most flexible in iMovie when you apply Fit, Crop, or Ken Burn effect.
Activity 1: Resizing a picture to 1920px x 1080px
- Open the file named music-performance.jpg.
- Go to Image -> Image Size;
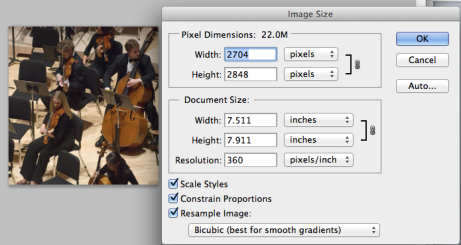
- Make sure all the three boxes at the bottom of the window are checked, Resample Image – Bicubic Sharper (best for reduction), change Height to 1080 pixels. Then click OK button.
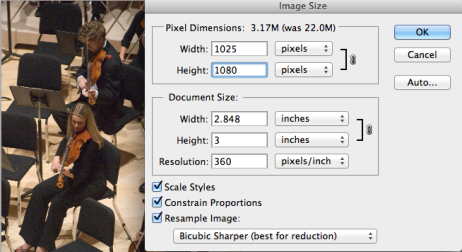
- Go to Image -> Canvas Size, change Width to 1920 pixels, make sure Black is selected as the Canvas extension color.
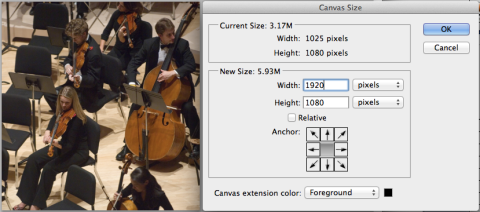
- Now you have a 1920x1080 picture with black bars on sides, which looks like the picture below. Go to File -> Save as…, Format – JPEG, Save as a copy, on the JPEG options window, Quality 8 High, then click OK button.

Enlarging pictures for print
This is a much more problematic process. Overall, enlarging an image above 200% should be avoided, since it results in much lower image quality.
When enlarging pictures for the purpose of print, the most important value is Resolution (in the Document Size part of the menu.). A good image quality can be achieved with printing resolution of 180 - 300 pixels/inch.
Activity 3: Resizing a picture 20in x 30in
- Open the file red-leaf.jpg.
- Image menu -> Image Size (or press Shift-Ctrl/-I.). Uncheck the box of Resample Image, put 300 for Resolution. Look at the Document Size in inches, which is what you can print with the current pixel dimensions.
- Then check the box of Resample Image, select Bicubic Smoother (best for enlargement). Put 20 inches for Height. Then click OK button.
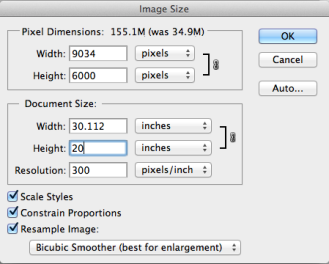
4. Or adjust the Document Size to what you want the physical size of your print to be. Check in the Pixel Dimensions part of the menu whether your new size is above 200%. If it is, you are strongly recommended to find a larger original image.
5. Go to File-> Save as, Format – JPEG, Save as a copy, on the JPEG options window, choose Quality 12 Maximum. Then click OK button. You want to preserve the highest quality you can.
Fixing and enhancing an image
Straighten an image
Activity 1: Straightening an image
- Open the file named Lovett-hall.jpg.

2. In the fly-out menu behind the dropper tool select the Ruler tool.
3. Click, hold, and drag to create a line across a part of an image that should be straight. Examples include rooftops of buildings and horizons.

4. Click the Straighten button in the options bar up top.
Touch up photos
Clone stamp tool
Activity 1: Using Clone Stamp tool to fix a picture
- Open the file named red-leaf.jpg.
- Select the clone stamp tool
 from the Tools menu, navigate to an area of the photo you want to duplicate, hold down ALT/Option and click.
from the Tools menu, navigate to an area of the photo you want to duplicate, hold down ALT/Option and click. - Release ALT/Option key, click and drag over the area you want to replace or correct. Play around with different brush settings and try replacing different areas of your photo until you get the hang of it.
- For instance, if you want to remove the twigs from the bottom. You can hold down the ALT/Option key and click an area close to that twig. Then release ALT/Option key, click and drag over the twig.
- The image before and after using Clone Stamp Tool.


Sponge tool
The Sponge tool allows you to use a brush to de-saturate or saturate certain areas of an image. De-saturation removes color and darkens an image and saturation adds more color and brightness. In the example photos below, the left one has been de-saturated except for around the pine needles, the middle is the original, and in the one on the right the grass has been saturated. Activity 1: Using Sponge tool to change the look of certain area of an image
- Open the file named lost-maples.jpg.
- Right click on the Dodge Tool to reveal the fly-out menu and select the Sponge tool
- Select Saturate or De-Saturate from the top menu
- Draw over the areas you want to adjust
- From left to right: after using De-saturate Sponge tool, the original, after using Saturate Sponge tool.



Spot Healing Brush
This tool can be used to make unwanted elements such as dark spots, bugs, etc., disappear just by clicking on them! Make sure to select "content aware" on the options bar. Use the bracket keys ([ ]) to adjust the size of the tool. You can also click, hold down and drag the cursor to remove longer objects such as cracks. See the images below.
Activity 1: Using Spot Healing Brush to remove blemishes(use girl-model.jpg)
- Open the file name girl-model.jpg.
- Click to select Spot Healing Brush
 .
. - On the options bar, choose the right size, check "content aware", then click over the blemishes on the model's face.
- Image before and after the use of Spot Healing Brush.


Before After
- Dragging to remove large spots such as cracks


Quick Selection tool
The Quick Selection Tool is somewhat similar to the Magic Wand in that it also selects pixels based on tone and color. But the Quick Selection Tool goes far beyond the Magic Wand's limited abilities by also looking for similar textures in the image, which makes it great at detecting the edges of objects. And unlike the Magic Wand where we click on an area and hope for the best, the Quick Selection Tool works more like a brush, allowing us to select areas simply by "painting" over them! Activity 1: Using Quick Selection tool to make a selection.
- Open the file named piano.jpg.
- Select Quick Selection tool
 , choose size 4.
, choose size 4. - Click inside the area of the first letter N.
- Hold down Shift key and click an area to add to the existing selected area.
- Hold down ALT/Option key and click an area to remove from an existing selected area.
- After you are satisfied with the selection of N, Ctrl/Command + C to copy it and Ctrl/Command + V to paste it.
- Select Move tool
 , drag the pasted N to the faded letter N.Note: The selection may be inverted by using Shift+Command+I. You can also add a new adjustment layer to make the desired changes
, drag the pasted N to the faded letter N.Note: The selection may be inverted by using Shift+Command+I. You can also add a new adjustment layer to make the desired changes

Lasso Tool (content aware)
The lasso tool allows you to make free-hand selections around objects you want to select. In this image we will use the lasso tool to select an ugly bush that we do not want in our photo and then use the Fill command to remove it.
- Outline an object you want to remove from a photo
- Select Edit>Fill, make sure "Use" is set to "Content Aware" and press OK.


Marquee Selection tools

The Marquee selection tools have the same functions as the Lasso Tool and Quick Selection Tool, but instead use fixed shapes where only the size of the shape can be adjusted.
- Rectangular marquee tool: This is the default selection setting. You can make a selection of any rectangular size and shape.
- Elliptical marquee tool: This tool, available when you click and hold down on the selection tool region of the tool bar, selects elliptical spaces. To select a round area, hold the shift key while clicking and dragging.
- Single row: This tool will select a 1pixel region that is as wide as your image. Very useful for trimming edges and making straight lines.
- Single column: The tool will select a 1pixel region that is as tall as your image. Also very useful for trimming edges and making straight lines.
Magic Wand Tool
The magic wand tool is similar to the lasso tool except that rather than dragging to make a selection, you click in a region and a selection appears around similar colored pixels. You can control how similar pixels must be to be included in the selection by altering the tolerance value. This tool is useful for selecting monochromatic regions or pieces of high-contrast images.
Adjusting exposure and level
- Brightness/Contrast layer
 : Adjusts the tonal range of the image. Brightness adjusts the highlights and contrast adjusts the shadows.
: Adjusts the tonal range of the image. Brightness adjusts the highlights and contrast adjusts the shadows. - Levels layer
 : Adjusts the shadows, midtones, and highlights.
: Adjusts the shadows, midtones, and highlights.
- Curves layer
 : Adjusts precise points in an image
: Adjusts precise points in an image
- Exposure layer
 :
:- Exposure adjusts the highlights
- Offset adjusts the midtones
- Gamma adjusts the dark tones only
- Vibrancy layer
 : Increases saturation, mostly on the least saturated colors
: Increases saturation, mostly on the least saturated colors
- Hue/Saturation layer
 : Allows adjustments of specific colors
: Allows adjustments of specific colors
- Color balance layer
 : Changes the mixture of colors.
: Changes the mixture of colors.- Add the brightness/contrast layer and adjust the brightness to -10
- Add the vibrancy layer and adjust to +15
Removing a background (use girl-model.jpg)
- Use the Quick Selection Tool and drag around the area you want to remove. When you have made your selection, right click and select Inverse (Shift+CMD+I).
- If your image is locked. Double click the pad lock icon to unlock it.
- Select Add Layer Mask
 in the layers panel.
in the layers panel. - Immediately you will see the background is gone.
- Right click on the mask in the layers panel and select Refine Mask.
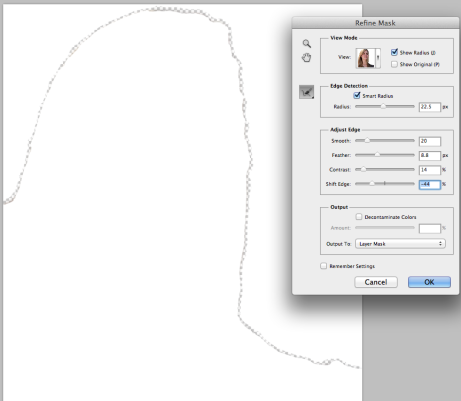
- Check Show Radius. There is nothing to begin with, but by adjusting the radius slider, you will see the radius is picking up all of the stray hairs and getting rid of the background between them. Uncheck Show Radius to go back to Refine Mask View mode.
- Adjust Edge be adjusting the sliders for Smooth, Feather, Contrast, and Shift Edge until you are satisfied with the look you've achieved. Then click OK button.
- If desired, add a new background by opening your desired one in Photoshop and dragging your cut-out image onto it.
- The original image and the image after removing the background:


Adding a new background to an image
- If your image has an existing background, remove it using the steps above
- For this demo use Lost-Maples.jpg as the background to place behind the girl model. Drag lost-maples into the Photoshop window with girl model open.

- Adjust the size of the image by using the curser to drag from the sides and corners. Make the necessary adjustments to make the portion of the image you want as the background fill the transparent areas.
- In the layers tab, drag the lost-maples layer down below the girl-model layer
- You might need to go through with tools such as the eraser tool and spot healing brush to fix minor blemishes to make the image look as good as possible. The end result should look similar to this:

Adding text and changing text color

- Placing text in the background
- Use the Text tool and draw a text box where desired. Select the font size and style from the top menu
- Select the Eraser tool. Zoom in on the areas to be erased to be more precise. Erase the areas of text that overlap the foreground objects so that the text looks like it is part of the scene.

- Changing Text Color and designs
- Select the text layer in the layers tab, then select the "FX" button at the bottom. In the fly-out menu select "Blending Options
- The "Layer Style" window will appear.
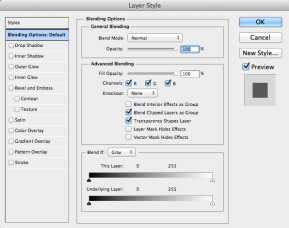
The box on the left gives many different choices for adjusting different features such as colors, shadows, and glow. Selecting them will bring up the options for adjustments to them in the center boxes of the window.
- Change opacity to 50%
- Drop Shadow: 80% Opacity and 150 degree angle
- Inner Shadow: 25% Opacity and 45 degree angle
- Bevel and Embross: 141% Depth, 128px size, 11px soften
Saving a transparent image (No Background color or image) Activity 1: Using Quick Selection tool to make a selection.
Open image named dmc-equipment.jpg;
Double click on the padlock icon in layer panel to unlock the image;
A window will appear asking you to name the layer. The default is "layer 0", but you can re-name it to whatever you wish.
3. Add a new transparent layer to an existing project by going to Layer>New>Layer. Name the layer and make sure Opacity is 0%. Press "OK." Drag the layer below the image layer in the layers window. 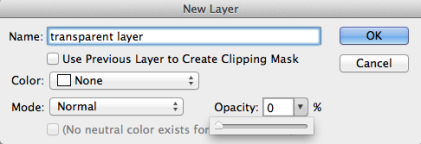
4. Select the dmc-equipment layer;

5. Use a tool such as the magic wand tool or lasso tool to select the areas you wish to make transparent. In this example, use the magic wand tool to select the background. You will see moving lines start circling around the objects in the image and around the border. If you need to add more to the selection hold down "SHIFT" and select the desired areas. If areas you do not want selected get selected, hold down "ALT/OPTION" and click on those areas to de-select. These are the same steps in the previous section of removing a background.

Once you have selected the areas then push the delete key.

The transparent part will be checkered. This pattern is not part of the image. It is just there to help you identify transparent areas.
6. Go to File>Save as… Format – PNG, and save it as a copy. Note: The JPEG format will not save transparent images.
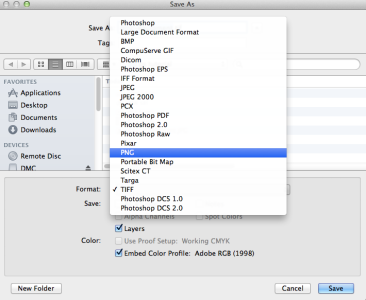
References and Resources
- Getting started with Adobe Photoshop https://www.ischool.utexas.edu/technology/tutorials/graphics/photoshop7/
- http://www.photoshopessentials.com
- Removing a background in photoshop http://www.digitalartsonline.co.uk/tutorials/photoshop/how-remove-background-in-photoshop/
- How to use typography with photography http://blog.slideshare.net/2014/03/31/how-to-use-typography-with-photography/
Toolbar Cheat Sheet
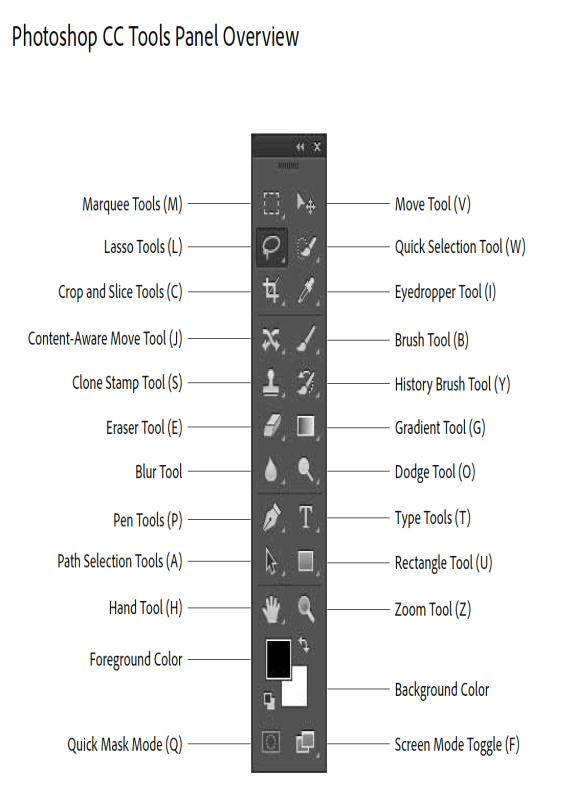
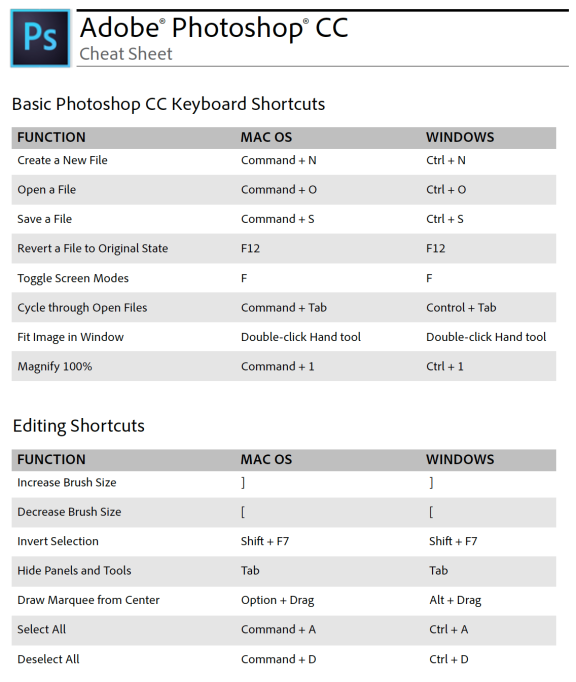
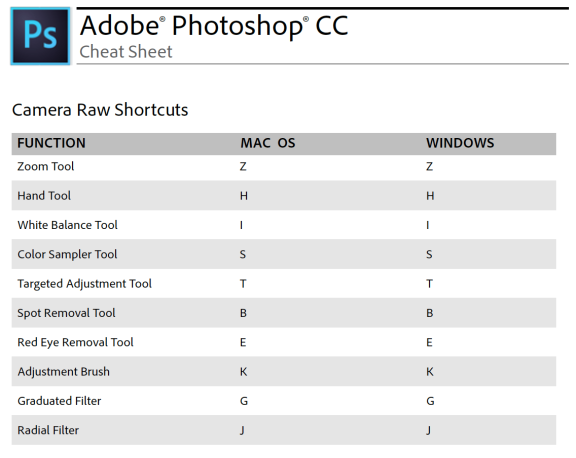






























![]()
![]()























