TABLE OF CONTENTS
This guide was created by the staff of the GIS/Data Center at Rice University and is to be used for individual educational purposes only. The steps outlined in this guide require access to ArcGIS Online software and data that is available both online and at Fondren Library. The following text styles are used throughout the guide: Explanatory text appears in a regular font.
Folder and file names are in italics. Names of Programs, Windows, Panes, Views, or Buttons are Capitalized. 'Names of windows or entry fields are in single quotation marks.' "Text to be typed appears in double quotation marks." |
The following step-by-step instructions and screenshots are based on the Windows 10 operating system and ArcGIS Online software with an Advanced license. If your personal system configuration varies, you may experience minor differences from the instructions and screenshots. |
Note: In order to use ArcGIS Online through Rice University, you must have a valid NetID and access to Duo Secruity.
Once you are signed into ArcGIS Online, you will see our organization's homepage, the header ribbon, and your ArcGIS Online account (see example below).

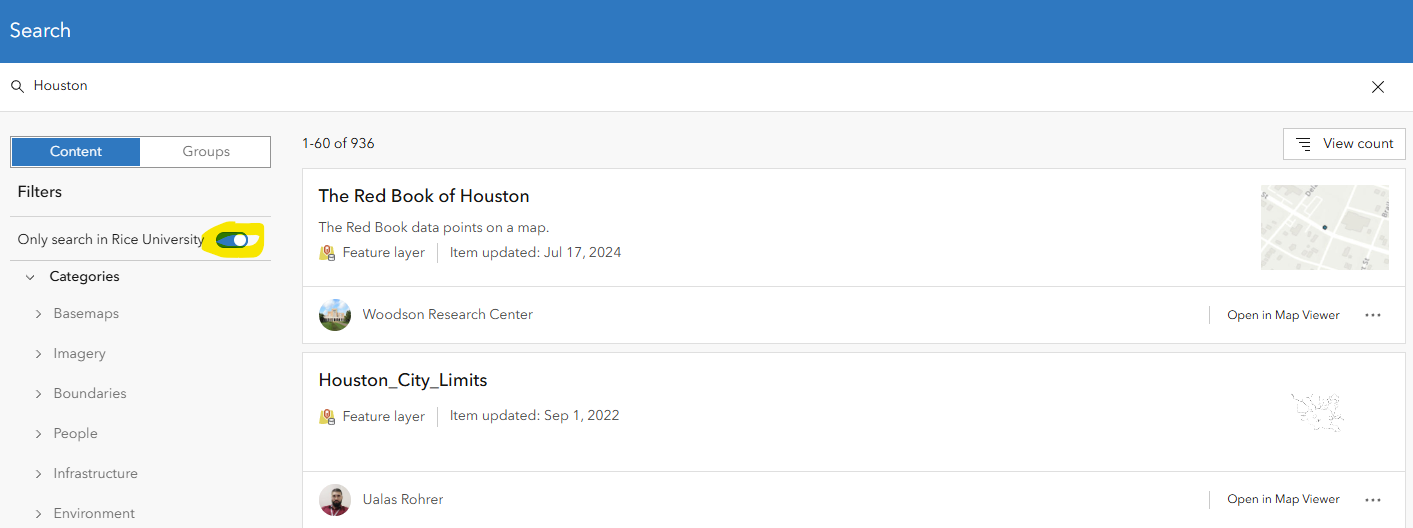
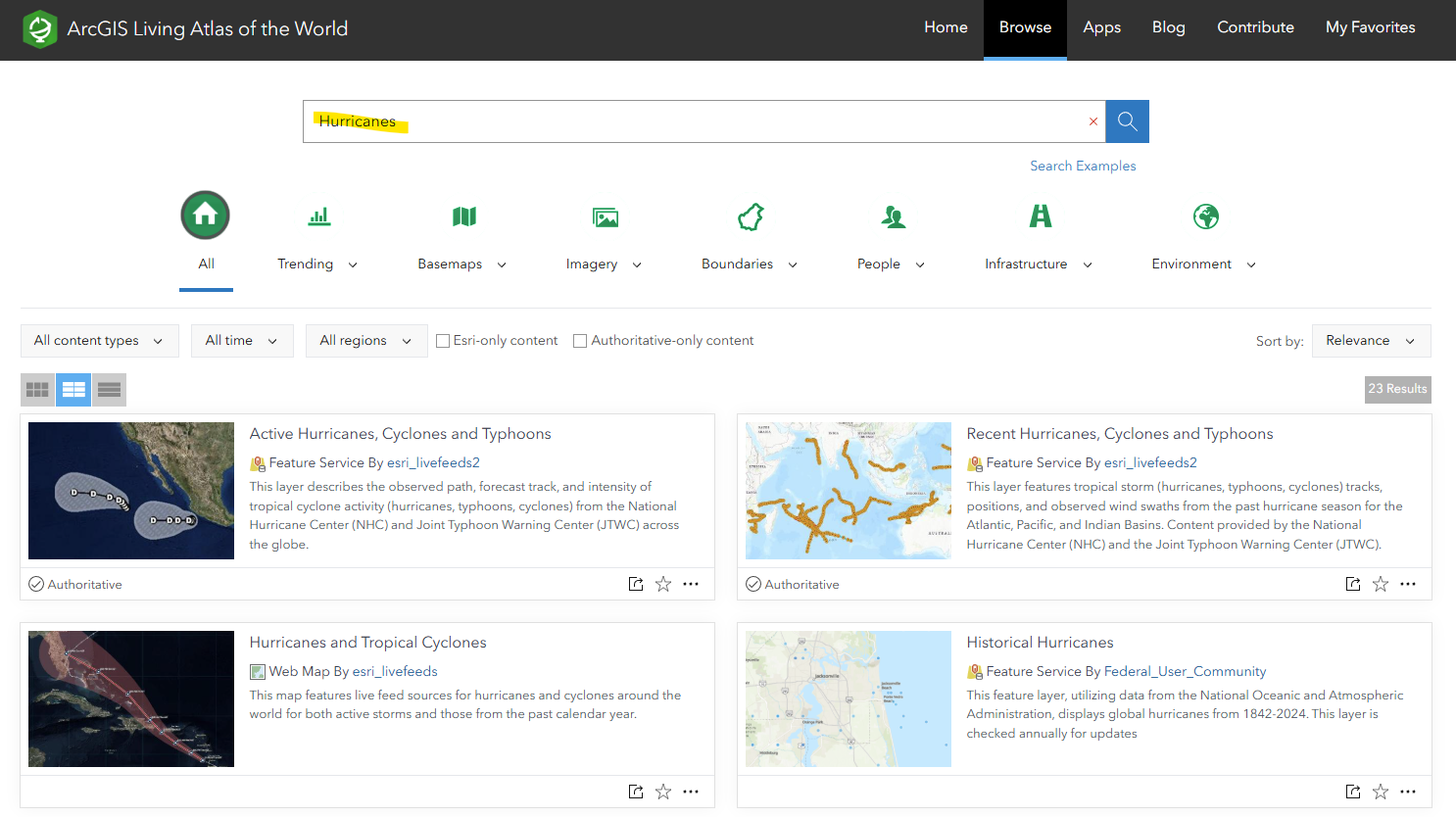
Uncheck the "Only search in Rice University" toggle to view the whole universe of content and data in ArcGIS Online. Try the search again with your own keyword(s). Note that you can filter by item type, sort by Relevence, Date, and popularity.
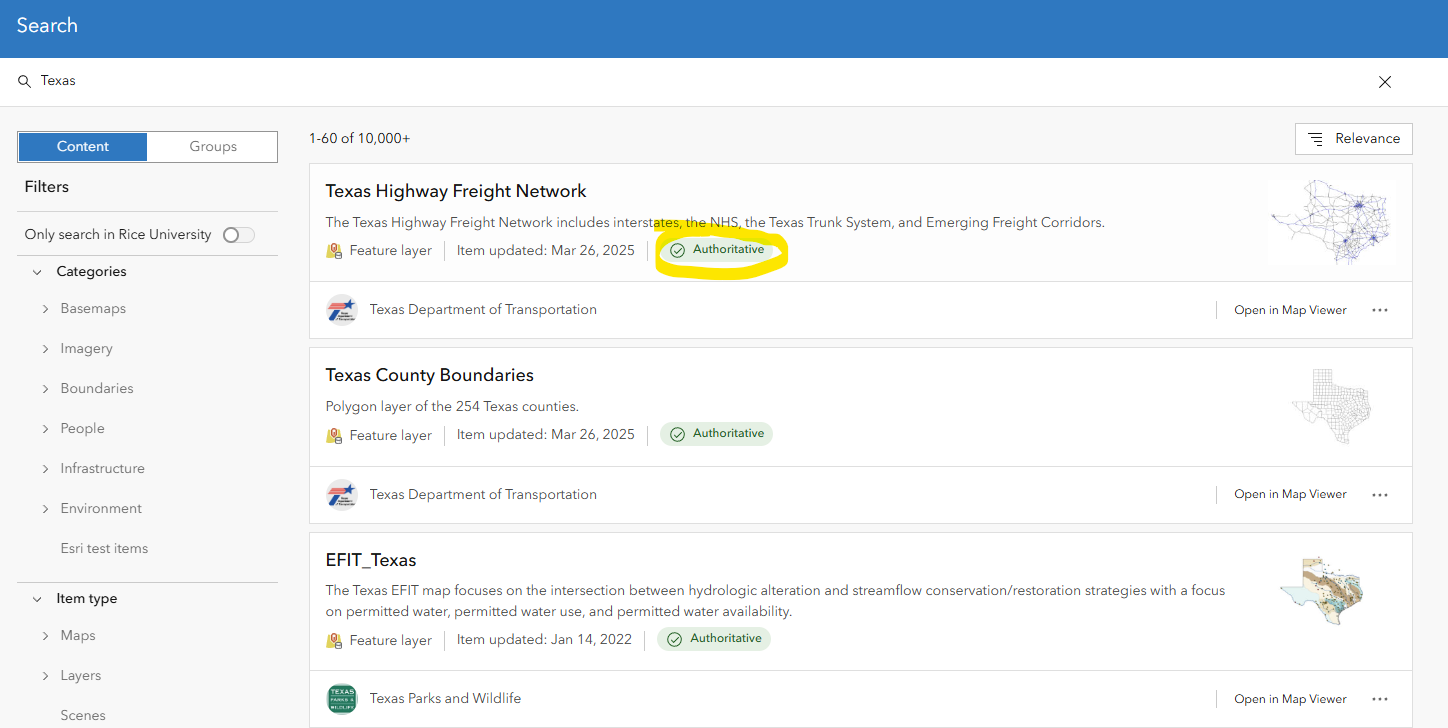
Some data is marked as "Authoritative", meaning it has been flagged as coming from a reliable source. Author content is marked with the "Living Atlas" flag, which shows it is part of ESRI's curated collection of updated data.
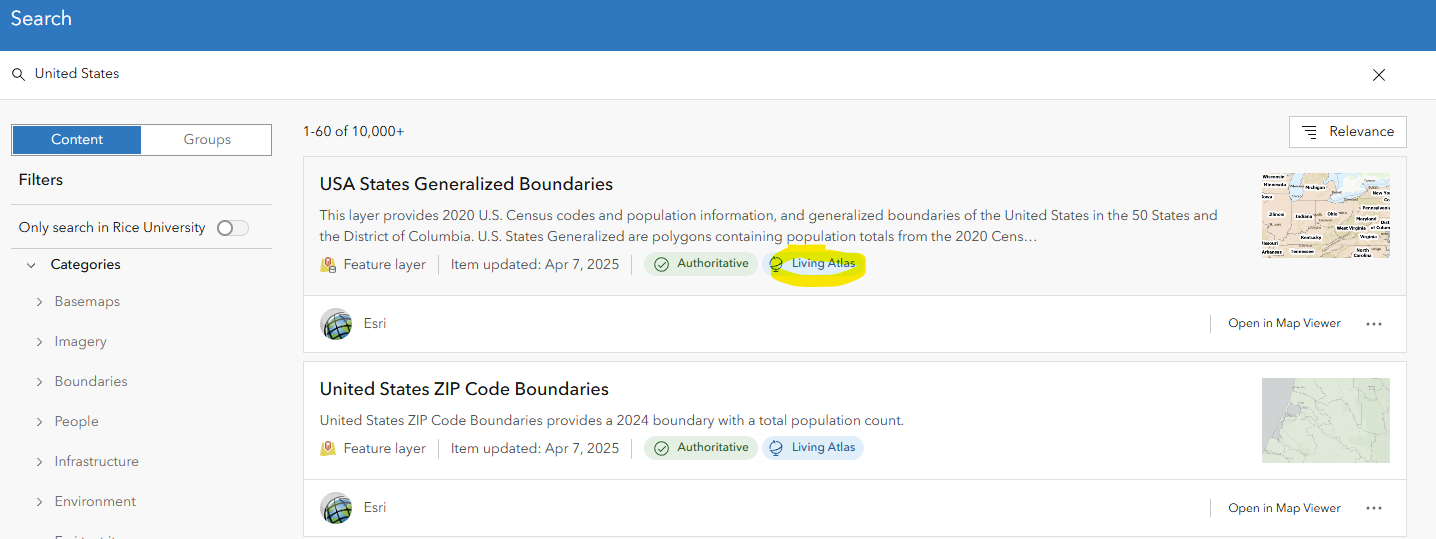
What is the Living Atlas? The Living Atlas is curated set of geospatial data, managed and distributed by ArcGIS's parent corporation, Esri. It includes basemaps, commonly-used geospatial layers, live data, satilite imagery, and more. Anyone can upload data and maps to ArcGIS Online, but the content in the Living Atlas is well-documented and comes from a reliable publisher of geospatial data, like a government agency.

You can search the Living Atlas in detail by
You can also filter your search using the to filter your results by type or theme.
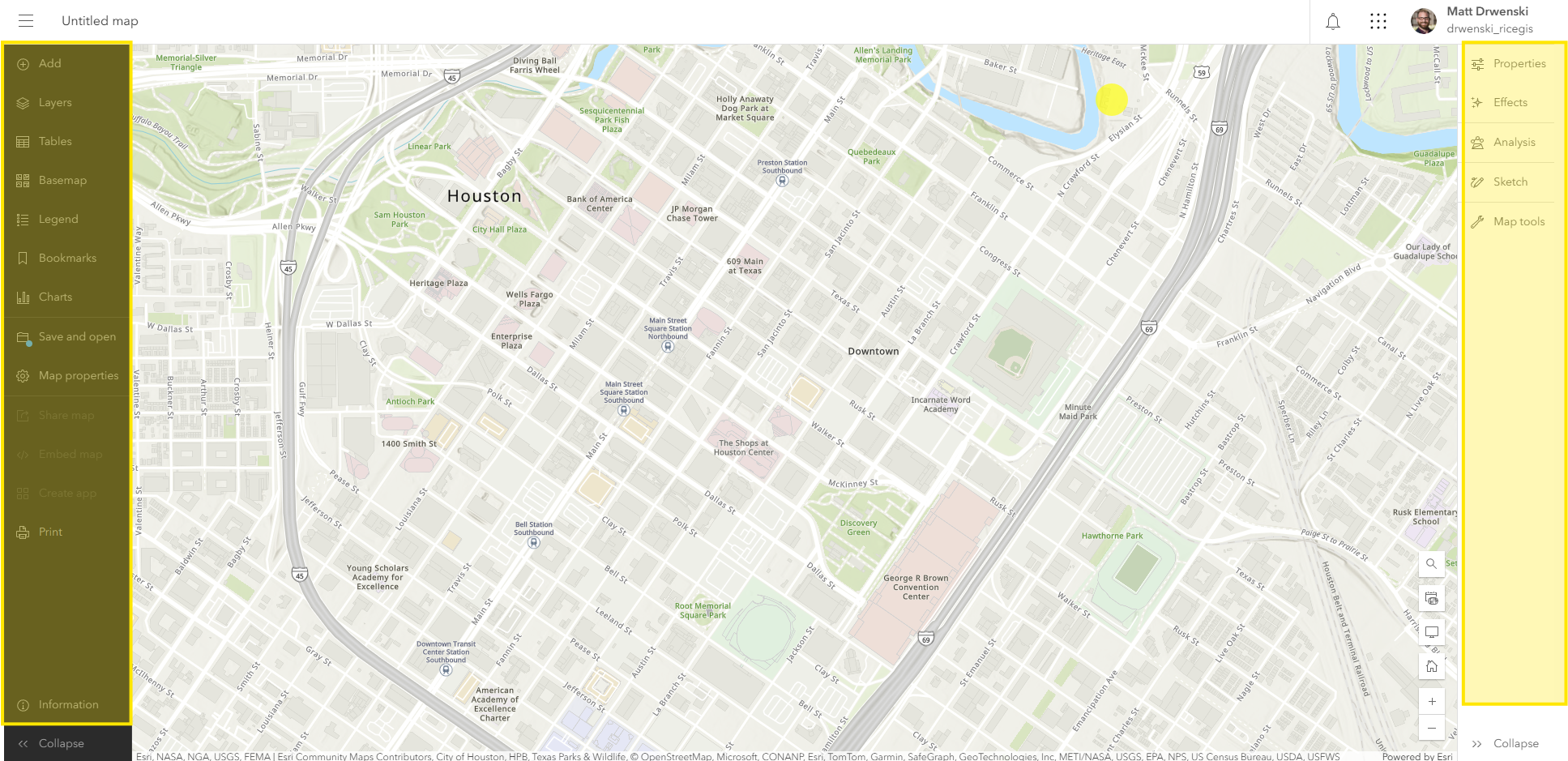
Overall we have two main menus in ArcGIS Online, the lefthand (dark) menu which generally applies to the whole map, and the righthand (light) menu which has specific functions based on what is currently selected. Both can be expanded and collapsed using the Expand/Collapse ">>" arrows at the bottom corners of the page.
On the lefthand (dark) menu, you'll notice a blue dot on the "Save and open" button. This appears when we've modified the map but not yet saved our changes. Since ArcGIS Online is browser-based, none of changes are saved until you save your project. Save your project now, but clicking the Save and open button and selecting Save as. Give your map a title, "Introduction to ArcGIS Online." You can add tags, categories, and descriptions to maps, or come back and add these later.
The righhand (light) menu, is contextual, it's options change based on what you have selected in the data sections of the righthand menu.
Let's add our first item to the map: a sketch layer. Sketch layers allow you to quickly add points, lines, or polygons to mark points of interest. You can also add text to the map. Unlike other layers, sketch layers are not permanent data layers and cannot be exported to other maps. Think of them as quickly drawing on top or your map when you need add a quick label or point of interest.
Note that as you zoom out, click your United States bookmark, the labels you have created become jumbled and inappropriate for this scale. You may also notice that your pins or text obscure important details you may want visible. You can solve this problem by adjusting the visibility and transparency of your sketch layer.

Last, it's very useful to turn off the visibility of layers that you are not actively working on. In the Layers lefthand (dark) menu, you can hide a layer by hovering over its name and clicking the "Hide Layer" (eye "👁" symbol) that appears. Your layer is still part of the map but its visibility is disabled until you click the 👁 button again.
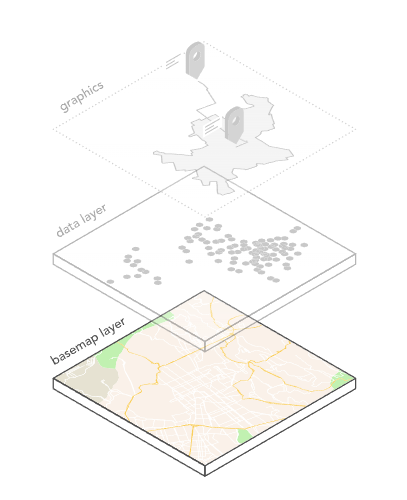
The basemap is a background reference image that provides context for your data. The basemaps here are created by Esri.
 on the lefthand (dark) menu.
on the lefthand (dark) menu. When selecting a basemap, consider the purposes and themes of the map, for some maps an imagery basemap might be best, for others a basemap with detailed roads and naviagtion features might be appropriate. For your training, select a neutral basemap, such as "Light Gray Canvas" so that we can focus on the data you will add to the map.
Adding data is the best way to use publicly available data or ready-map information for visualization or analysis. In subsequent trainings, you will learn how to add your own data ArcGIS Online.

Your map now has this collection of geospatial layers with attached data on vehicle availability collected from the American Community Survey. Let's explore how to look at this dataset in ArcGIS Online. Then, we will prepare this data for a map that visualizes Harris County, Texas.
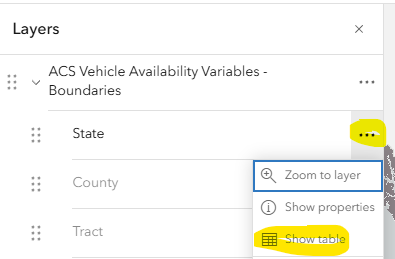
This data is feature layer. The layer contains shapes or polygons (the States of the U.S.) and data attached to each of these shapes. With the table open, you can see that it's organized like spreadsheet: each row represents a polygon (State) and each column represents a field of the data (such as "state Name, Total Households, etc.). Scroll down to see more of the states until you reach Texas to the scroll right to see more of the fields in this layer until you find Total Households. You can see that that there are over 10 million households in Texas.
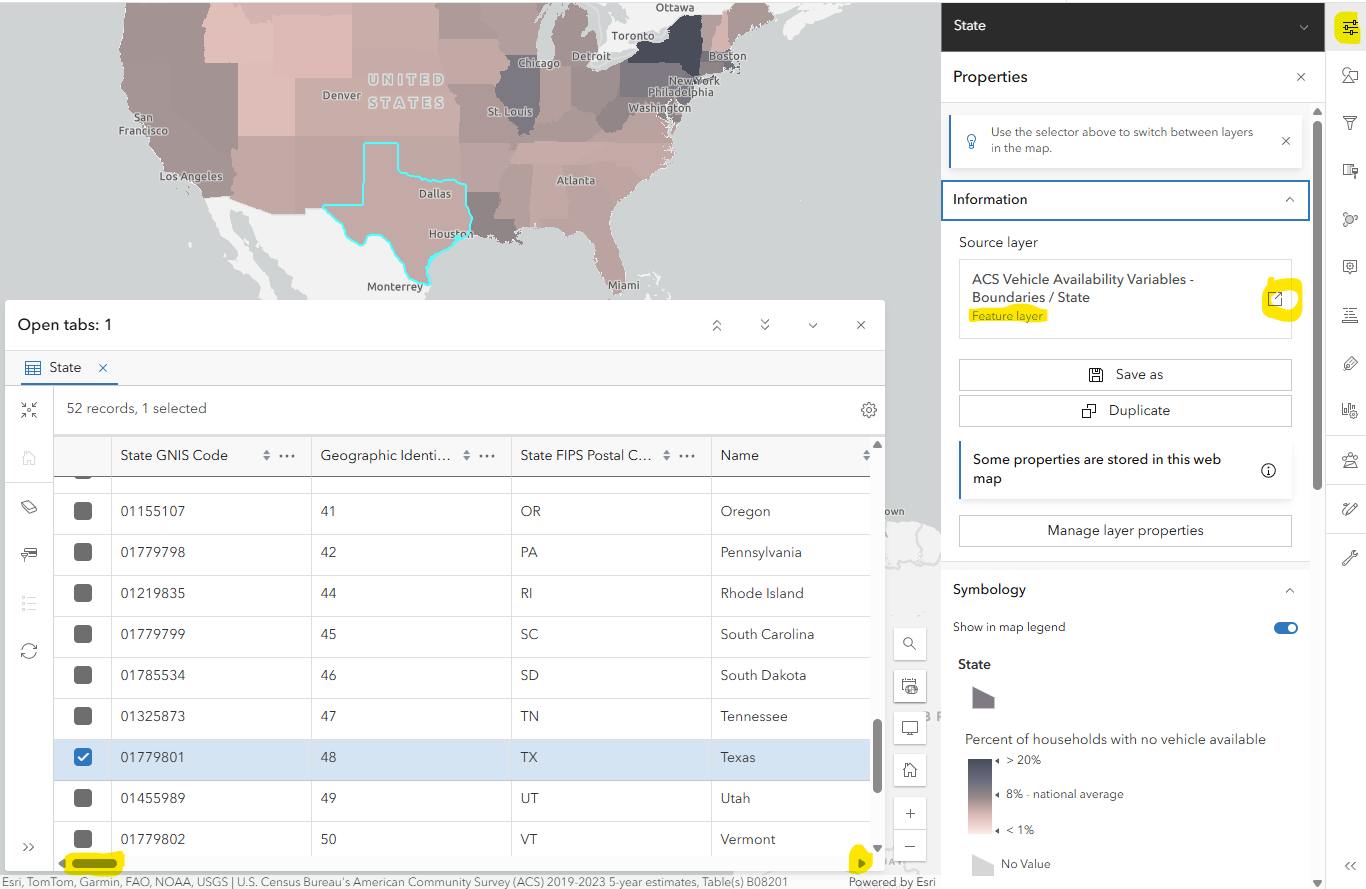
Click the properties button (first button on the righthand (light) menu with the layer selected) and expand the Information submenu. Under Source layer click the name "ACS Vehicle Availability Variables - Boundaries / State" to open the details page for this layer.
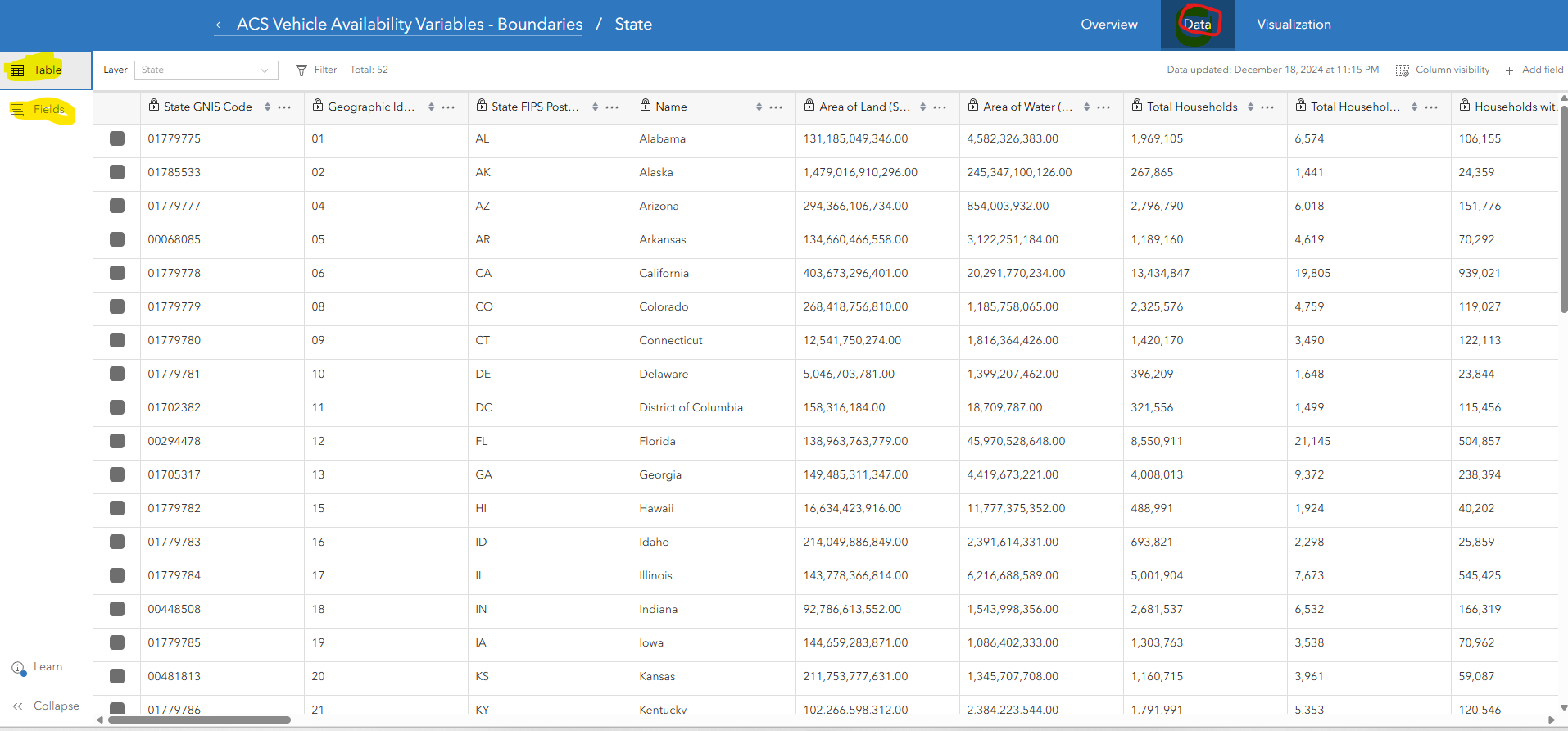
Here you can see any additional metadata (description, owner, acknoledgments, etc.) and by moving to the Data seciton in the top ribbon, you can explore the table in a full page fiew as well as read through a list Fields (button on the left) and see if the field is identifier, a string (text), or a numberic value (Integer, or Double) as well as its value type. ArcGIS treats each of these field types differently and allows you to run different types of vizualizations and analysis on different field types. Here, in the Table view, you can also quickly sort by each field, filter fields, or hide columns.
A Polygon feature layer, like this layer of States, is just one type of geospatial data. As you progress in your training, you'll also in points (emission sites or trees, for example), in polylines (streets or rivers, for example), or polygons (congressional districts or

You may have noticed that the scope of this group of layers with data on Vehicle Availibility goes well beyond our goal of a vizualization of Harris County, Texas. In order to trim and focus our data, we will group our layer, rename our layer, and run a filter on our layer.
This data is a Grouped Layer, containing individual layers for States, Counties, and Census Tracts. Since the scope of our vizualization is Harris County, our study just needs the data from Tracts in order to identify areas that might have low vehicle availability. To ungroup the layer, either grab with your cursor the six dots on the left of the layer name and drag it out of the group, or click on the three dots on the right of the Group Layer name and click ungroup. Remove the unneeded layers, by clicking the three dots to the right and selecting "Remove."

To group layers, simply click the three dots on the the right and select Group to start a new group of layers.
This data
Grouping and Ungrouping Layers
Renaming Layers
Removing Layers
You can also duplicate a layer
Create a filter and Adust Visibility
Duplicate Layer, Rename Layer (Total Households)
Select a Field
What's in a Layer?
Quickly Add another Layer
Play around with Styles
Save and Sharing Settings
Breakout Room
ACS
Georeferencing LatLong Data
Add a new Item
Upload a file
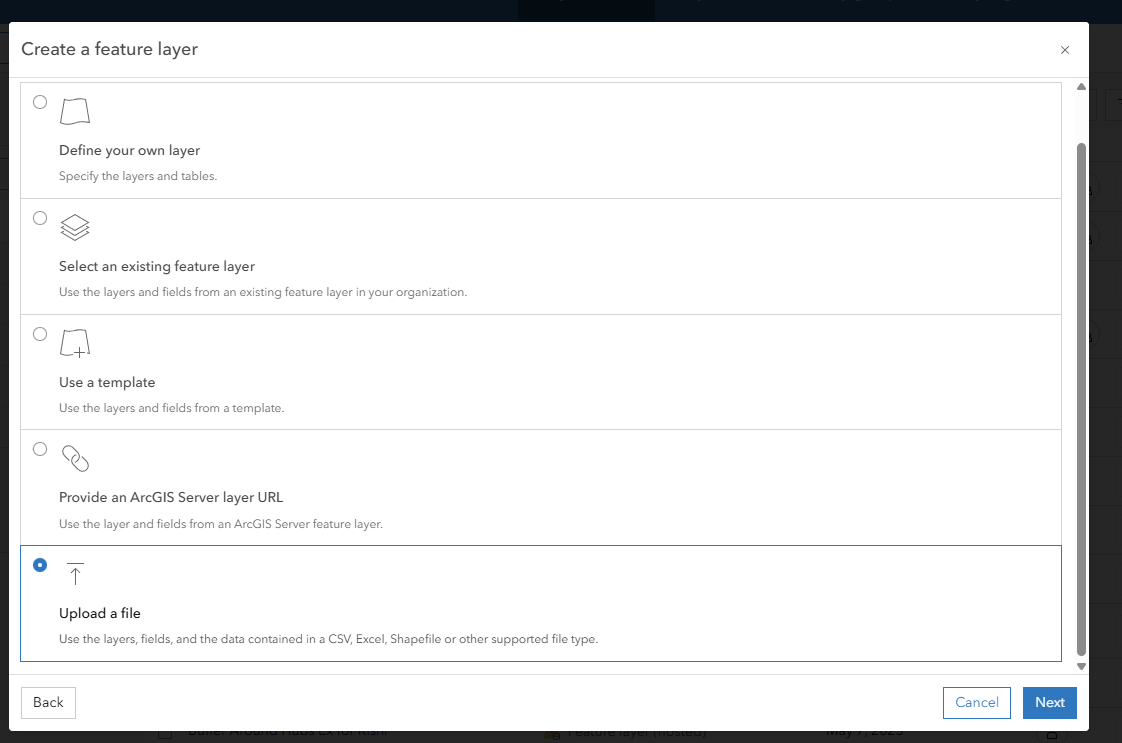
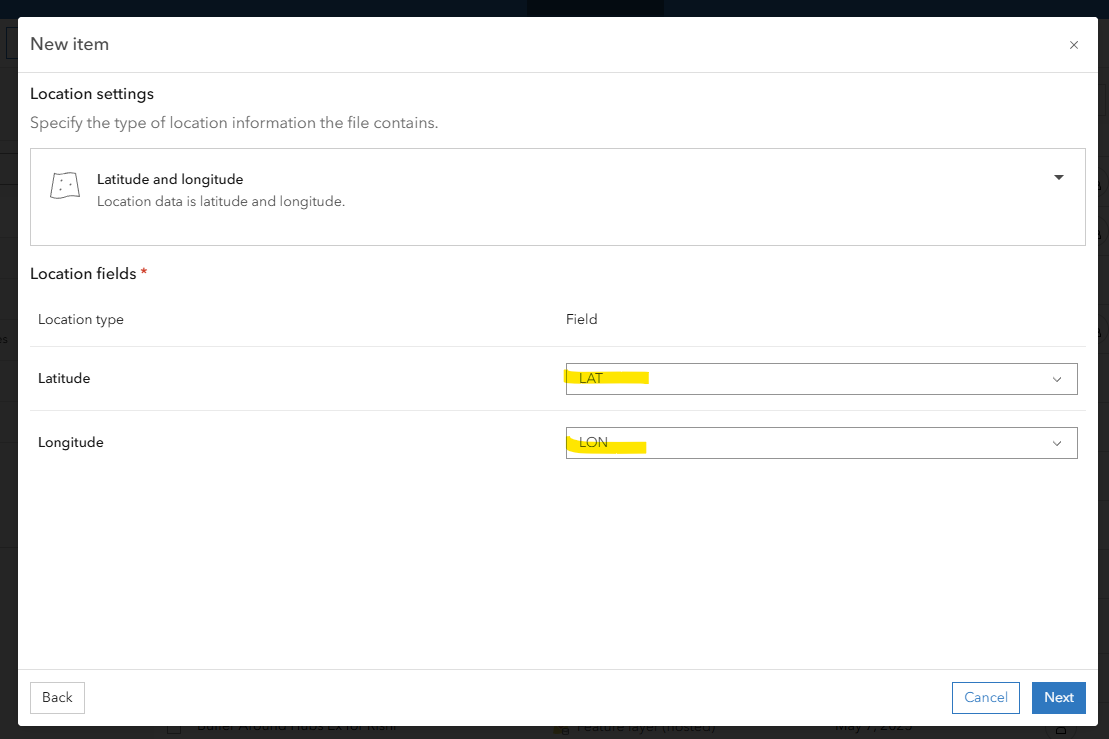
Identify Latitute and Longitude data
Global Average Wind Speeds by Month and Altitude
https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=3de721e9c4d84e72ac65c761f7d47668


Add hospital Data
https://ricegis.maps.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=77087d6c494141b4929418a765a00505
Labels
Charts
Hospital Beds
Aggregate Points Tool
https://doc.arcgis.com/en/arcgis-online/analyze/aggregate-points-mv.htm
Goals:
Intro:
Temp Outline
FUTURE: Creating a Layer with Lat/Long, Creating a Layer with Georeferencings (After upgrading everyone to publisher)
Future: Explaining Point, Line, Polygon. Vecter/Raster/Image
Future: Popups and Charts
Navigating a Layer Data
Layers:
"ACS Vehicle Availability" ESRI
COH METRO BUS STOPS
Houston Census Tract Demographics
Houston Freeways
Operations:
Summarize Within