...
On the Desktop, click the Start menu and select ArcGIS > ArcGIS Pro.
- If the 'ArcGIS Sign In' window appears, sign in using your Rice organizational account. (Detailed Instructions)
- In the ‘ArcGIS Pro’ window, under the 'New' section, select the Map template.
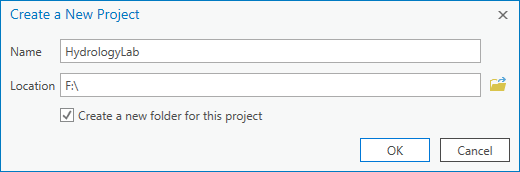
- In the ‘Create a New Project’ window, for 'Name', type " HydrologyLab ".
- For 'Location', click the Browse button.
Navigate to the location in which you would like to store your HydrologyLab project folder and click OK.
inInfo A A project folder folder is where you will store all of the files associated with this lab assignment. When working in a public computer lab environment, we recommend saving your work on an external USB drive. If you wish to nest your project folder inside other folders on your USB drive, or if you are using the hard drive on personal computer, ensure that no spaces or special characters are used anywhere along the entire file path of your your project folderfolder. The default project location on your personal computer is C:\Users\[ username ]\Documents\ArcGIS\Projects.
In order to connect to a folder, you often have to be able to select
listingthe folder from the file
browser on the right, rather than in the Navigation pane on the left. For example, if you wanted to store the project on an external USB F:\ drive, you would need to single-click Computer in the Navigation pane on the left and then single-click F:\ in the file browser on the right.
- Once the HydrologyLab folder is selected, click OK.
- Ensure Create a new folder for this project is checked.
- Click OK.
Because you created a new project using the Map template, the project opens with a single map already created; however, it is generically named Map, so you will give it a more descriptive name to differentiate it from the maps created in future labs.
...
- If necessary, in the 'Filters' section on the left sidebar, toggle off Only search in Rice University, at which point the proper layer should appear.
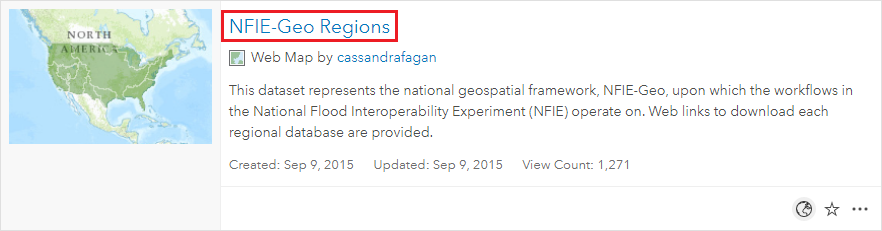
- Click the NFIE-Geo Regions web map.
- On the right, click to Open in Map Viewer.
- On the map, click to select the Texas-Gulf region, which encompasses Houston.
- In the pop-up, click More info.
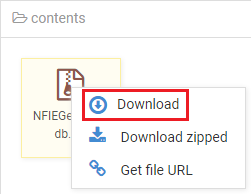
- In the Content section, right-click the NFIEGeo_12.gdb.zip file and select Download.
- Navigate to the location where the zipped file has been downloaded.
- Right-click the downloaded NFIEGeo_12.gdb zip file and select Extract All….
- In the ‘Extract Compressed (Zipped) Folders' window, click Extract.
- In the new extracted folder window that opens, right-click the extracted NFIEGeo_12.gdb folder and select and Copy.
- Navigate back to your HydrologyLab folder.
- Paste the NFIEGeo_12.gdb folder directly inside your HydrologyLab folder. Do NOT paste them inside the HydrologyLab.gdb geodatabase.
- Ensure that your HydrologyLab folder appears as shown below.
- Return to ArcGIS Pro.
Adding feature data in ArcMap
...
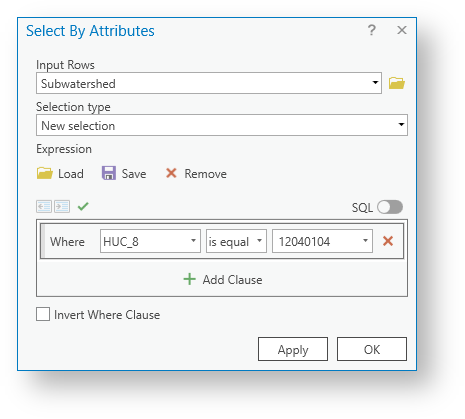
- On the Map tab, click the Select by Attributes button.
- In the 'Select By Attributes' window, use the ‘Input Rows’ drop-down menu to select the Subwatershed layer, if necessary.
- Use the ‘Selection Type’ drop-down menu to select New selection.
- Click New expression.
- For the first two fields, select HUC-8 , and is equal to .
- Type "12040104" in the last field.
- Verify that your ‘Select By Attributes’ window appears as shown below and click OK.
- In the Contents pane, right-click the Subwatershed layer and select Selection > Zoom To Selection.
...
- For ‘Output Name’, type “ SubwatershedsNew ”.
- Ensure your ‘Export Features’ window appears as shown below and click OK.
Since you’ve exported the particular subwatersheds of interest, you may now remove the master Subwatersheds layer from your map.
...
- For ‘Input Features’, drag in the SubwatershedsNew layer from the Contents pane or select the SubwatershedsNew option from the drop down box.
- For ‘Output Feature Class’, rename the feature class from “SubwatershedsNew_Dissolve” to “ Subbasin ”.
- For ‘Dissolve_Field(s)’, select the HUC_8 field, since this is the field containing the common subbasin value you wish to dissolve on.
- Ensure your ‘Dissolve’ tool appears as shown below, and click Run.
- In the Contents pane, toggle the new Subbasin layer off and on to get a better idea of the result of the Dissolve tool.
- In the Contents pane, right-click the Subbasin layer and select Attribute Table.
...
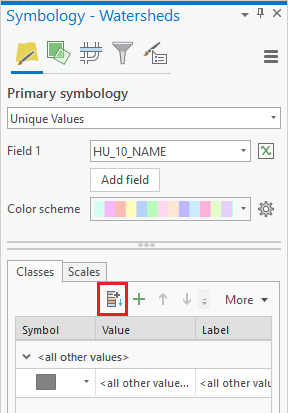
- In the Contents pane, right-click the Watersheds layer and select Symbology.
- In the Symbology pane, use the 'Primary symbology' drop-down menu to select Unique Values.
- Use the ‘Field 1’ drop-down menu to select the HU_10_NAME field.
- Use the ‘Color Scheme’ drop-down menu to select the color ramp of your choice.
- On the bottom half of the Symbology pane, if only one category called <all other values> is listed, as shown below, click the Add all values button.
...
- At the top left of your Layout view, click the Lab1Hydrology map tab to return to your map view.
- In the Contents pane, check the Flowline and Catchment layers to make them visible.
...
- On the ribbon, click the Map tab.
- In the Selection group, click the Select By Location button.
- For ‘Input Features’, use the drop-down menu to select the Flowline layer.
- Use the second 'Input Features' drop-down menu to select the Catchment layer.
- For ‘Relationship’, use the drop-down menu to select Have their center in. (This setting ensures that catchments and flowlines which share the outside border with the subbasin will not also get selected.)
- For ‘Selecting Features’, use the drop-down menu to select the Subbasin layer.
- Ensure your ‘Select by Location’ window appears as shown below and click OK.
All of the flowlines and catchment areas that are within the subbasin are now selected.
...
- At the top left of your map view, click the Layout tab to return to your layout view.
- On the ribbon, click the Insert tab.
- In the Graphics and Text group, click the Rectangle text button.
- Drag a rectangle on your map layout to insert a rectangle text element.
...
- Return to the Lab1Hydrology map view.
- Open the Flowlines Symbology tab.
- Use 'Primary Symbol' drop down menu to select Graduated symbols.
- Use the ‘Field’ drop-down menu to select the Q0001C field, which contains the mean annual flow.
- Click the line next to Template to change the symbology of your flowlines.
- Save your project.
FOR MAP LAYOUT TO BE TURNED IN
...
- Return to the Layout view.
- On the ribbon, click the Share tab and click the Layout button in the Export group to open the Export Layout pane on the right.
- In the Export Layout pane, use the 'File Type' drop-down menu to select PDF.
- For 'Name', type "Lab 1 Hydrology" and click Export.
- Save your project.
FOR MAP LAYOUT TO BE TURNED IN
...
- Click the SSURGO Downloader web mapping application.
- On the right side of the webpage click the View Application button.
- In the search bar in the top corner, type "Houston, TX".
- Click in the Buffalo-San Jacinto subbasin to select it and click the Download link.
- Right-click on your downloaded BuffaloSanJacinto_12040104.ppkx file and select Show in folder. Copy the file.
- Navigate back to your HydrologyLab folder.
- Paste the BuffaloSanJacinto_12040104.ppkx file directly inside your HydrologyLab folder. Do NOT paste it inside the Hydrologylab.gdb geodatabase.
- Single-click the .ppkx file to select it and press Enter.
...
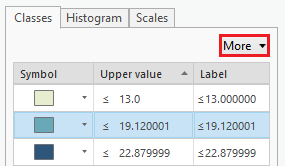
- On the bottom half of the symbology pane, click the More drop-down button and select Formal all symbols.
- Use the ‘Outline Color’ drop-down menu to select No Color.
- Click Apply.
...
- What is the average available water storage (cm) in the Buffalo-San Jacinto subbasin?
- Based on your previous calculation of the area of the subbasin in km2, what volume of water (km3) could potentially be stored in the top 1 m of soil in the Buffalo-San Jacinto subbasin if the soil were fully saturated with water?
Deliverables
- Create an 8.5 x 11 layout with the following layers limited to the subbasin:
...